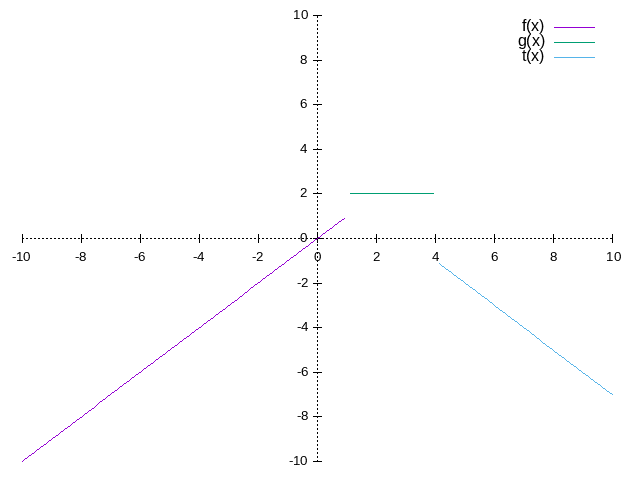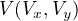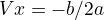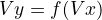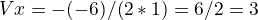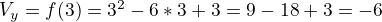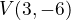Polynomial
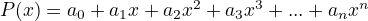
- examples of polynomials:
![\[\begin{align*}
f(x) &= 2x^3 + 3x^2 + 7x - 3 \\
g(x) &= x^4 + 3x + 4 \\
t(x) &= x
\end{align*}\]](/ltximg/math_4543b7a102e6c61faae0d26edfa52692bbab6f4c.png)
Constant
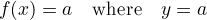
-
Dependent variable,
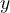 , has always the same value for all values of
, has always the same value for all values of 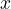 , independent variable.
, independent variable. -
It’s a horizontal line
-
example:
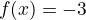
x y 0 -3 1 -3 3 -3 4 -3 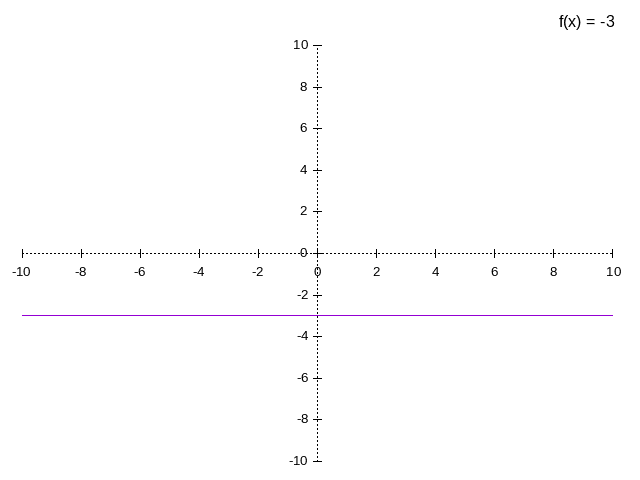
Affine
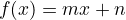 where
where 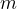 is the slope and
is the slope and 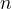 the origin of ordinates.
the origin of ordinates.
-
It is a polynomial function.
-
Grade 1
-
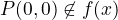
-
example:
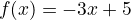
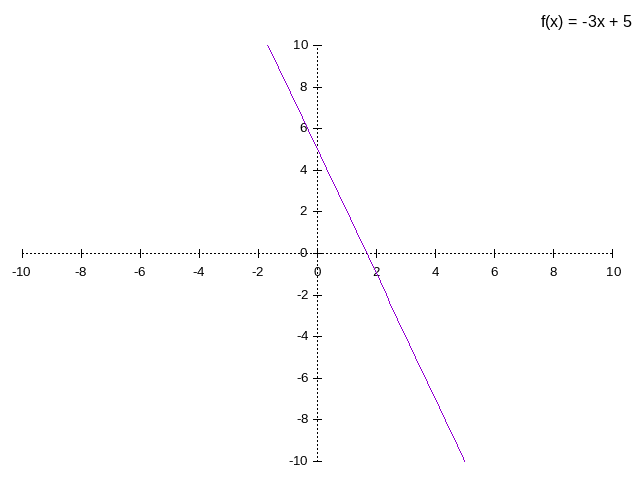
Lineal
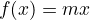
-
It is a polynomial function.
-
Grade 1.
-
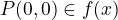
-
example:
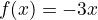
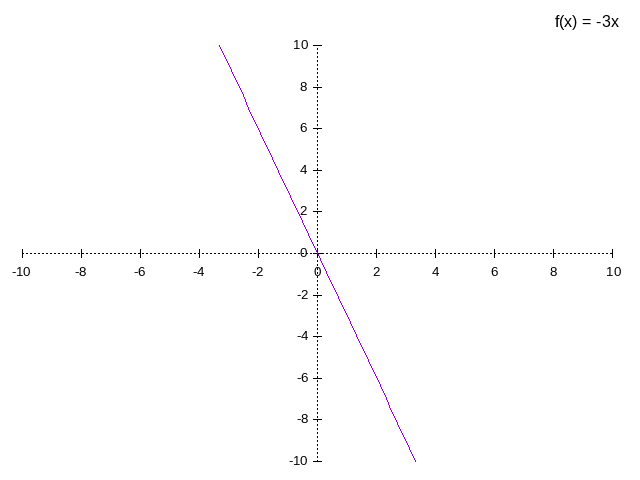
Identity
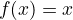
-
image of
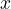 is always
is always 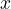
-
It is a polynomial function.
-
Grade 1.
-
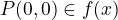
-
the slope,
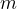 , is always 1.
, is always 1. -
example:
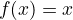
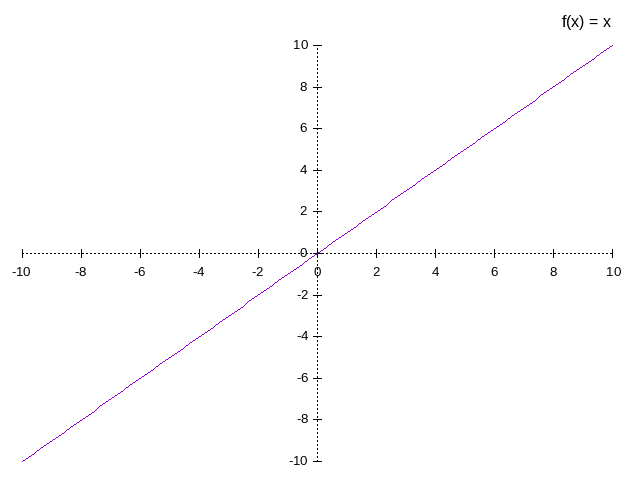
Quadratic
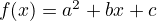
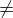
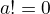
-
They have always a vertical parabole shape.
- a > 0 ,, concave \/
- a < 0 ,, convex /\
-
Find parabole vertex
-
example:
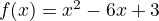
- Calculate vertex of
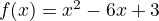 :
:
-
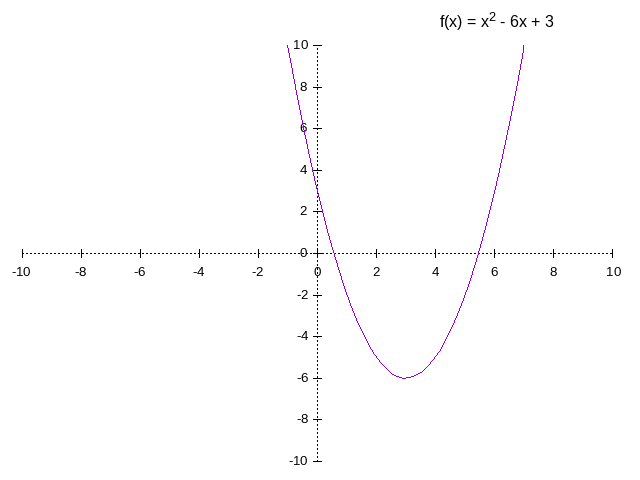
- Calculate vertex of
Cubic
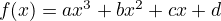
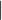
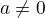
-
example:
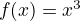
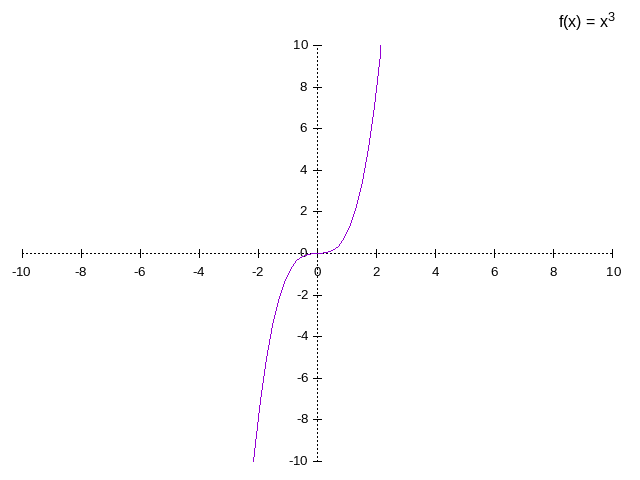
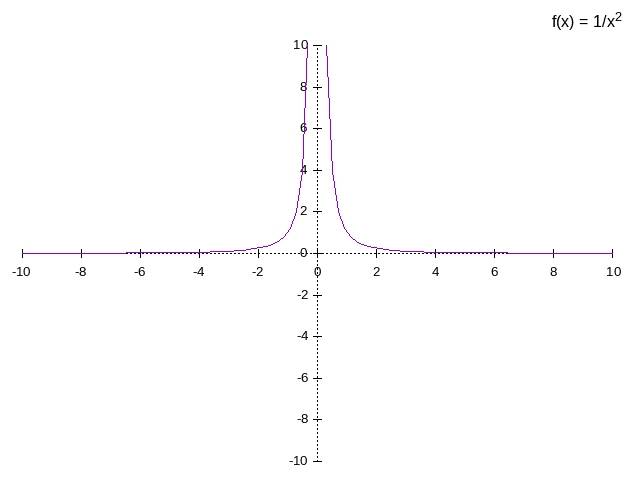
Rational
![\[f(x)= \dfrac{P(x)}{Q(x)}\]](/ltximg/math_f4bf8bc83729fd907ed5e2f07f9a63f8fc255747.png)
-
P grade and Q grade can be different
-
when P grade is equal to Q grade => horizontal asymptote
-
when Q grade is greater than P grade => horizontal asymptote
-
when y, P grade is greater in one unit than Q grade => oblique asymptote
-
example:
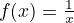
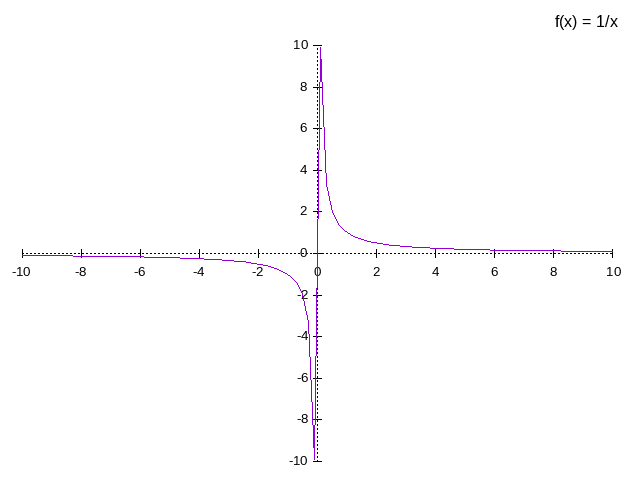
-
example:
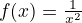
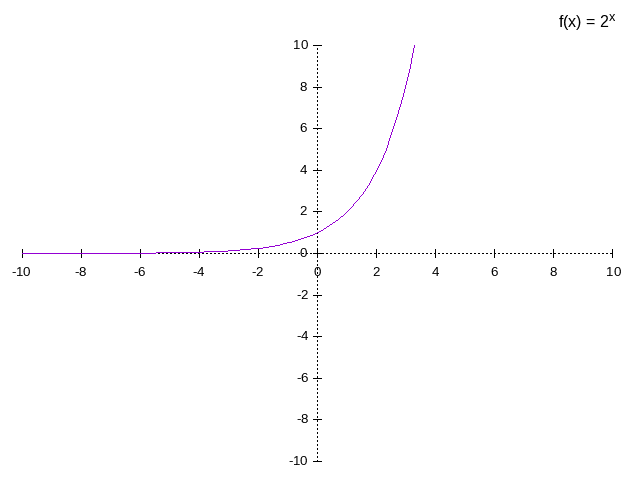
Exponential
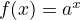
-
if a > 0 funtion goes up
-
if a < 0 function goes down
-
if x > 0 fuction goes right
-
if c < 0 fuction goes left
-
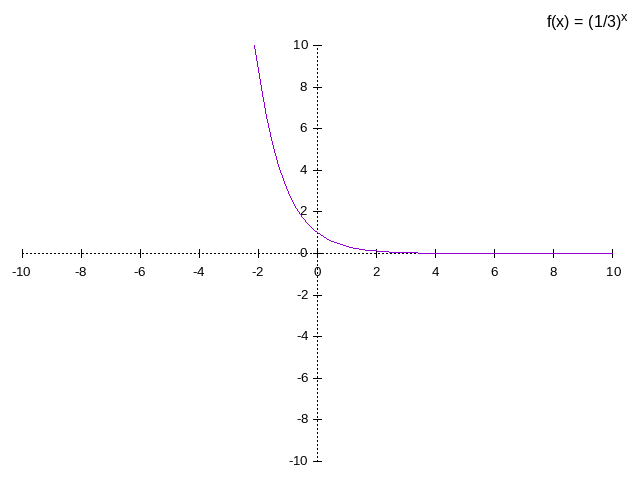
example,
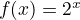
- example,
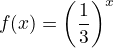
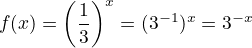
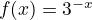
- x < 0, then to left
- 3 > 0, then up
- example,
Logarithm
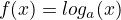
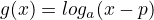
-
there is a vertical asymptote and it is where (x) = 0. in
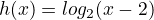 , the asymptote is in
, the asymptote is in 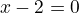 then
then 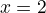 .
. -
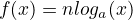
- x > 0, to the right
- n > 0, up
-
example:
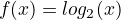
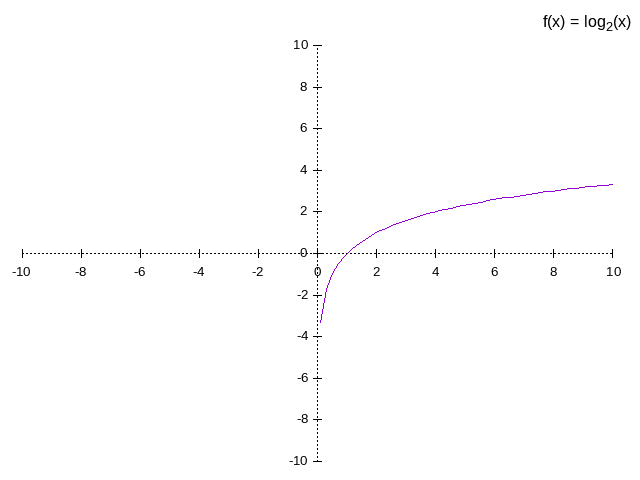
Trigonometrical
-
basic trigonometrical functions are sin(x), cos(x) and tan(x).
-
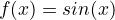
x y π/2 1 π 0 3π/2 -1 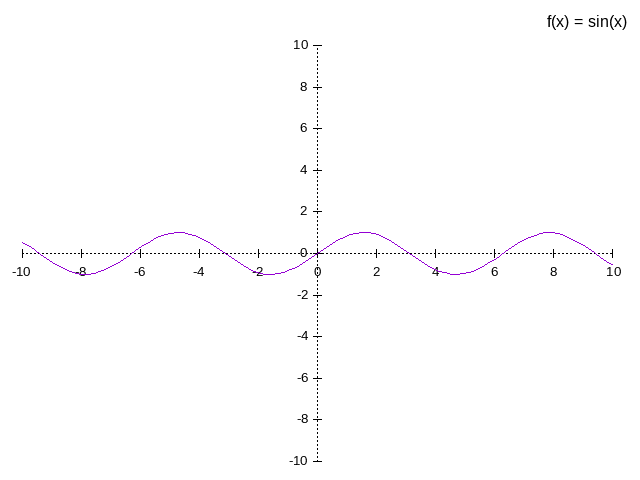
-
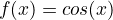
x y 0 1 π/2 0 π -1 3π/2 0 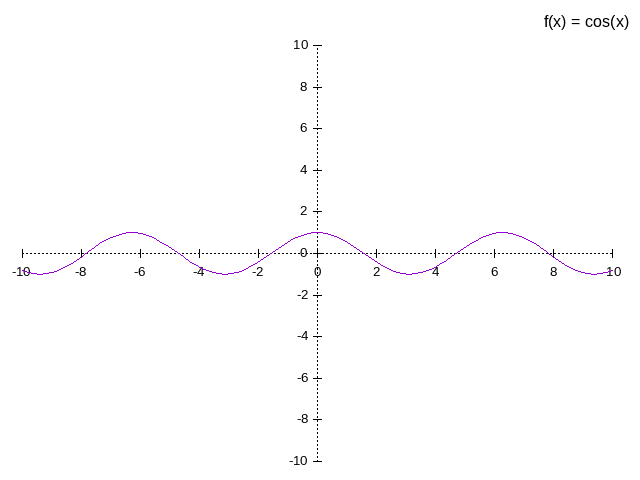
-
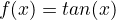
x y 0 0 1 1.55 -1 -1.55 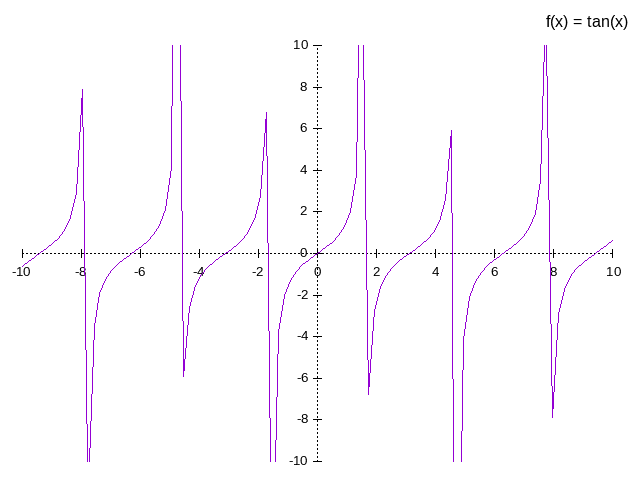
Discontinuous
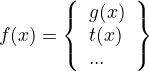
-
example:
![\[
f(x) = \left\{
\begin{array}{lr}
x+3, & x \le 1 \\
x-2, & x>1
\end{array}\right\}
\]](/ltximg/math_051bdd384afbdb8704a7713eab0fda2c41a3b77b.png)
x+3 x y 1 4 0 3 -1 2 x-2 x y 1 -1 2 0 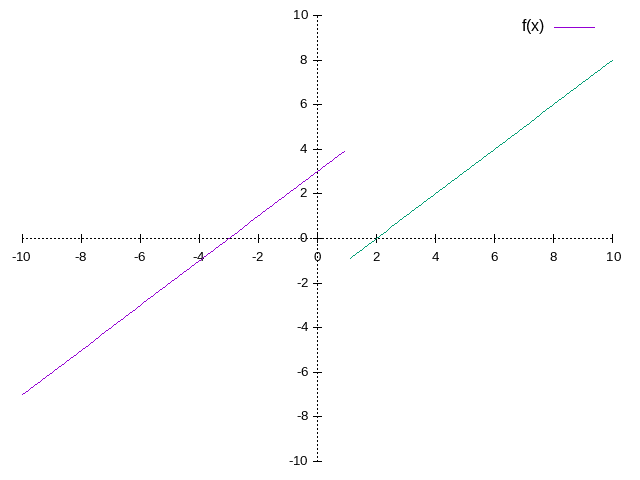
-
example:
![\[
f(x) = \left\{
\begin{array}{lr}
2, & x \le 0 \\
x^2+2, & x>0
\end{array}\right\}
\]](/ltximg/math_b447f9bf34d58c06b9a06e70552bc78db9551c24.png)
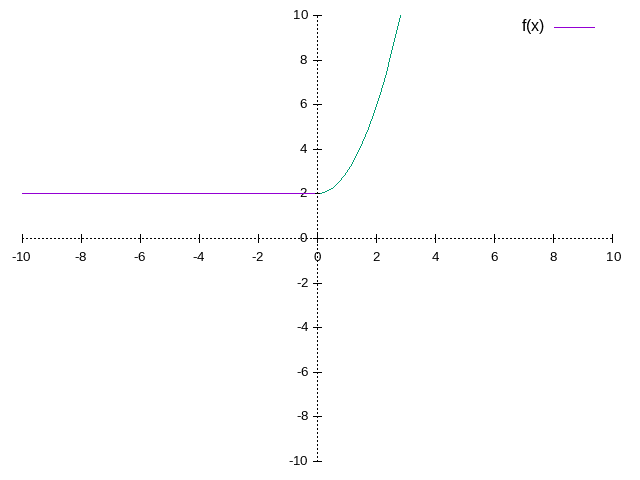
-
example:
![\[
f(x) = \left\{
\begin{array}{lr}
x, & x < 1 \\
2, & 1 \le x \le 4 \\
3-x, & 4 < x
\end{array}\right\}
\]](/ltximg/math_1bba5e58bd1b8a48ea4f2be68e3638a736543a83.png)